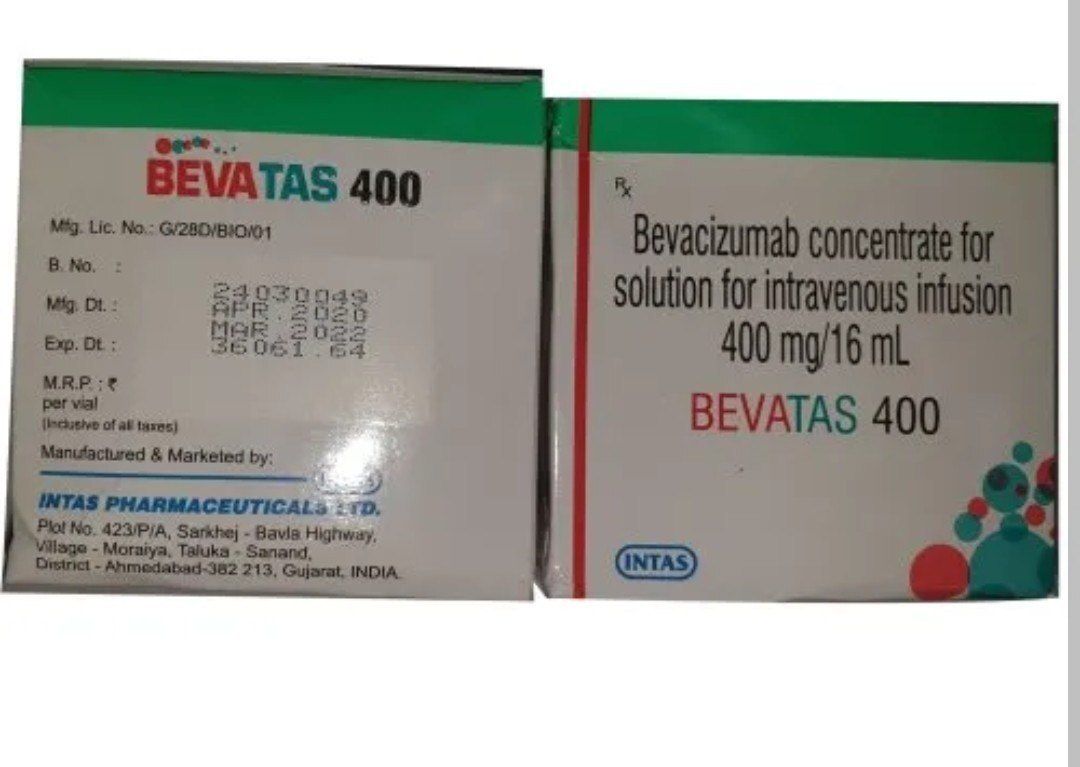
Bevacizumab Concentrate For Solution For Infusion
Product Details:
Bevacizumab Concentrate For Solution For Infusion Price And Quantity
- 5 Vial
- 9500 INR/Vial
Bevacizumab Concentrate For Solution For Infusion Trade Information
- Cash Advance (CA) Cash in Advance (CID)
- 1000 Vial Per Week
- 4 Days
- Asia Australia Central America North America South America Eastern Europe Western Europe Middle East Africa
- All India South India Central India West India North India East India Gujarat Karnataka Kerala Lakshadweep Mizoram Meghalaya Manipur Andhra Pradesh Bihar Chandigarh Daman and Diu Goa Jharkhand Odisha Punjab Assam Delhi Dadra and Nagar Haveli Andaman and Nicobar Islands Arunachal Pradesh Chhattisgarh Haryana Himachal Pradesh Jammu and Kashmir Madhya Pradesh Maharashtra Nagaland Rajasthan Sikkim Tamil Nadu Telangana Tripura Pondicherry Uttar Pradesh Uttarakhand West Bengal
Product Description
Bevacizumab concentrate for solution for infusion, with a strength of 400 mg/16 mL, is a medication used in the treatment of various types of cancer. Here's an overview of its use:
1. Colorectal Cancer Bevacizumab is approved for use in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC). It is typically used in combination with a fluoropyrimidine-based chemotherapy regimen (such as FOLFOX or FOLFIRI).
2. Lung Cancer Bevacizumab is also used in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), specifically in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced, metastatic, or recurrent NSCLC. It may be used in patients who have not received prior chemotherapy for metastatic disease.
3. Breast Cancer Bevacizumab may be used in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, particularly in cases where the cancer is HER2-negative.
4. Renal Cell Carcinoma Bevacizumab, in combination with interferon alfa, is used for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer).
Bevacizumab is a monoclonal antibody that targets vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein involved in the formation of new blood vessels that supply tumors with oxygen and nutrients. By inhibiting VEGF, bevacizumab helps to disrupt the blood supply to tumors, thereby slowing their growth and reducing their ability to spread.
The concentration of 400 mg/16 mL indicates that each mL of the solution contains 25 mg of bevacizumab. This solution is typically diluted further and administered as an intravenous infusion over a period of time specified by a healthcare professional.
Common side effects of bevacizumab may include hypertension (high blood pressure), proteinuria (protein in the urine), bleeding, gastrointestinal perforation, impaired wound healing, and increased risk of blood clots. It's important for patients to be monitored closely by their healthcare provider while receiving bevacizumab to manage any side effects and ensure the treatment remains effective.
As with any cancer treatment, it's crucial to discuss the potential benefits and risks with a healthcare professional to make informed decisions about treatment options.

Price:
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+










 Contact Us
Contact Us
